Bootstrap Modal Validation
Introduction
In some cases we absolutely should make the concentration on a specific information leaving everything rest turned down behind to make confident we have really captured the site visitor's focus or maybe have lots of data needed to be accessible directly from the page still, so vast it absolutely would bore and dismiss the person browsing the webpage.
For these events the modal feature is absolutely priceless. What it does is showing a dialog box utilizing a great area of the display diming out anything else.
The Bootstrap 4 framework has all the things required for producing this sort of element using least initiatives and a practical direct construction.
Bootstrap Modal is streamlined, though variable dialog prompts powered by JavaScript. They maintain a lot of use samples starting with user notification ending with totally customized web content and provide a variety of useful subcomponents, scales, and far more.
Tips about how Bootstrap Modal Validation works
Before beginning having Bootstrap's modal element, ensure to read the following as long as Bootstrap menu decisions have currently reformed.
- Modals are constructed with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are actually positioned over everything else within the documentation and remove scroll from the
<body>- Clicking the modal "backdrop" will quickly finalize the modal.
- Bootstrap just supports one modal pane at once. Nested modals usually aren't supported as we believe them to remain unsatisfactory user experiences.
- Modals use
position:fixeda.modal- One once more , because of the
position: fixed- And finally, the
autofocusKeep reading for demos and application instructions.
- As a result of how HTML5 identifies its semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute provides no effect in Bootstrap modals. To get the exact same result, put into action certain custom-made JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)To start off we require a trigger-- an anchor or switch to be clicked so the modal to get displayed. To perform so simply assign
data-toggle=" modal"data-target="#myModal-ID"Some example
Now let's create the Bootstrap Modal itself-- primarily we require a wrapping component including the whole aspect-- appoint it
.modalA good idea would certainly be as well bring the
.fadeYou would definitely in addition like to provide the similar ID which in turn you have actually specified in the modal trigger considering that usually if those two do not suit the trigger probably will not actually launch the modal up.
If this has been done we require an special component holding the real modal content-- appoint the
.modal-dialog.modal-sm.modal-lg.modal-content.modal-header.modal-bodyAdditionally you might probably really want to add a close button inside the header appointing it the class
.closedata-dismiss="modal"Pretty much this id the construction the modal parts have inside the Bootstrap framework and it practically has kept the similar in both Bootstrap version 3 and 4. The brand-new version includes a bunch of new methods though it seems that the dev team expected the modals function all right the method they are in this way they made their attention off them so far.
Right now, lets take a look at the several kinds of modals and their code.
Modal elements
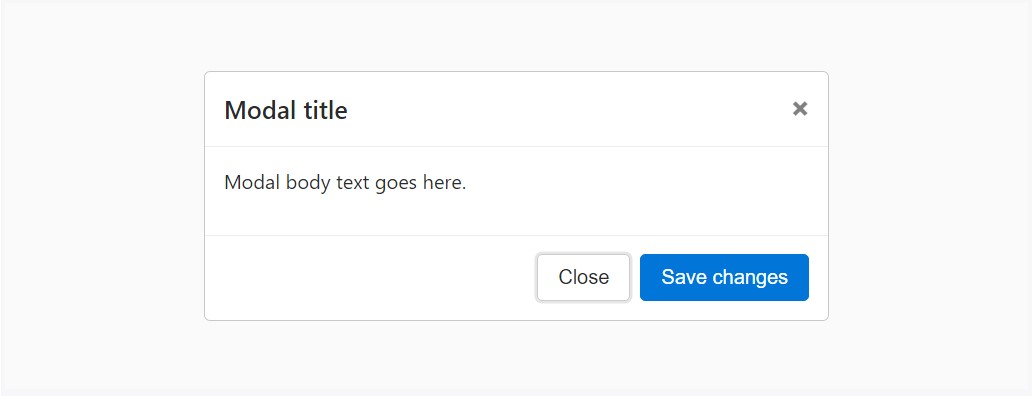
Listed here is a static modal example ( signifying the
positiondisplaypadding<div class="modal fade">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Modal body text goes here.</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Live demonstration
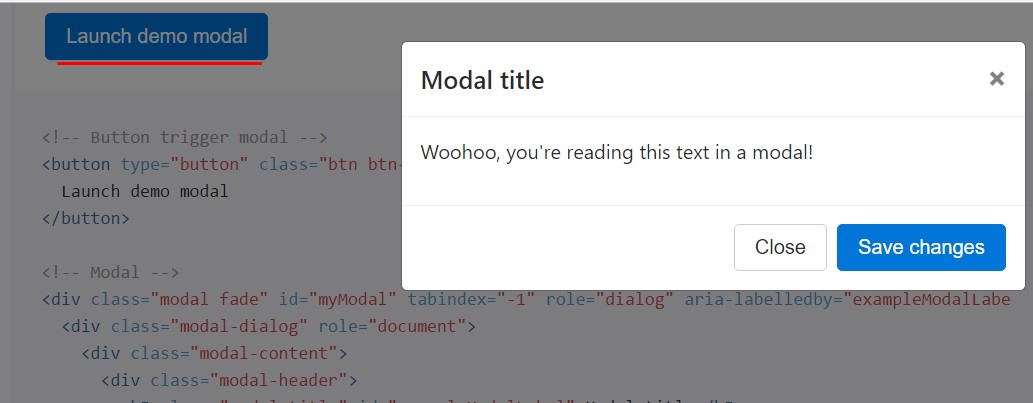
Whenever you will employ a code listed here - a functioning modal test is going to be activated as showned on the picture. It will definitely go down and fade in from the high point of the web page.
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Scrolling long text
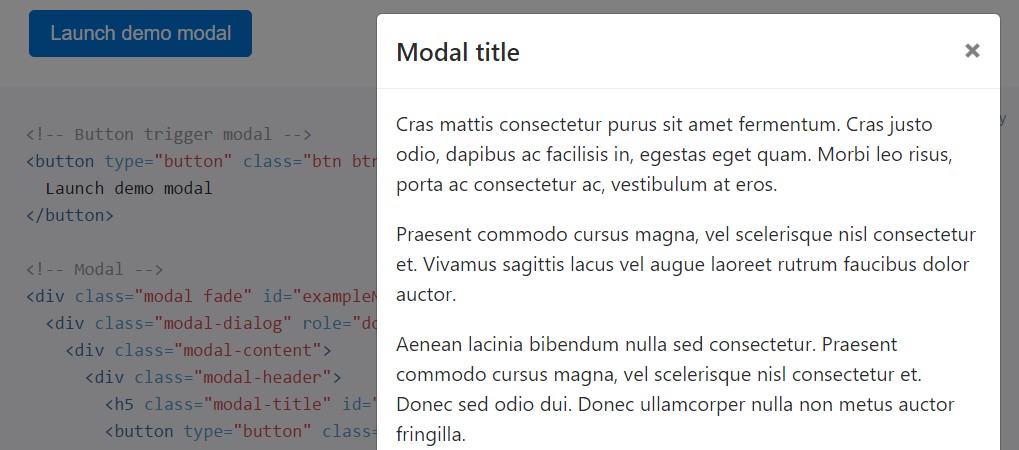
They scroll independent of the page itself when modals become too long for the user's viewport or device. Go for the demo listed below to discover exactly what we point to (read this).
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModalLong">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModalLong" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLongTitle" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLongTitle">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Tooltips plus popovers
Tooltips and popovers have the ability to be placed inside modals just as needed. Once modals are closed, any tooltips and popovers inside are as well automatically dismissed.
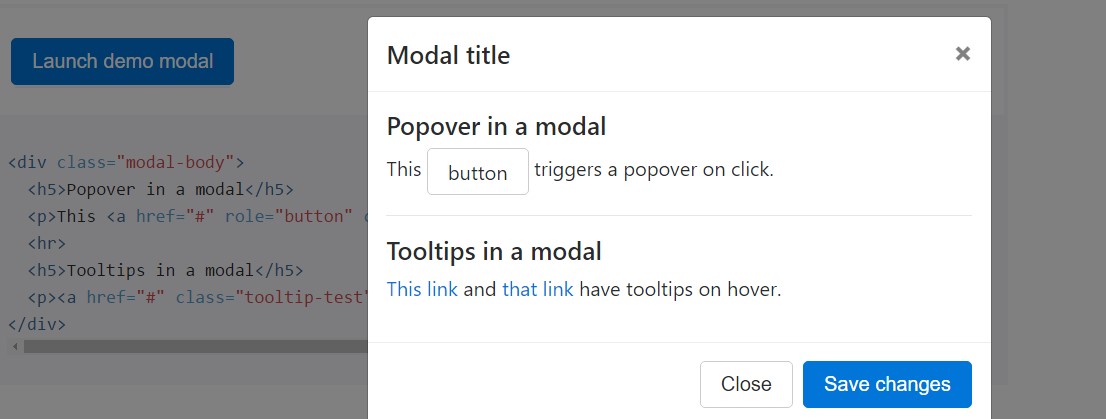
<div class="modal-body">
<h5>Popover in a modal</h5>
<p>This <a href="#" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary popover-test" title="Popover title" data-content="Popover body content is set in this attribute.">button</a> triggers a popover on click.</p>
<hr>
<h5>Tooltips in a modal</h5>
<p><a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">This link</a> and <a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">that link</a> have tooltips on hover.</p>
</div>Bring into play the grid
Implement the Bootstrap grid system inside a modal by nesting
.container-fluid.modal-body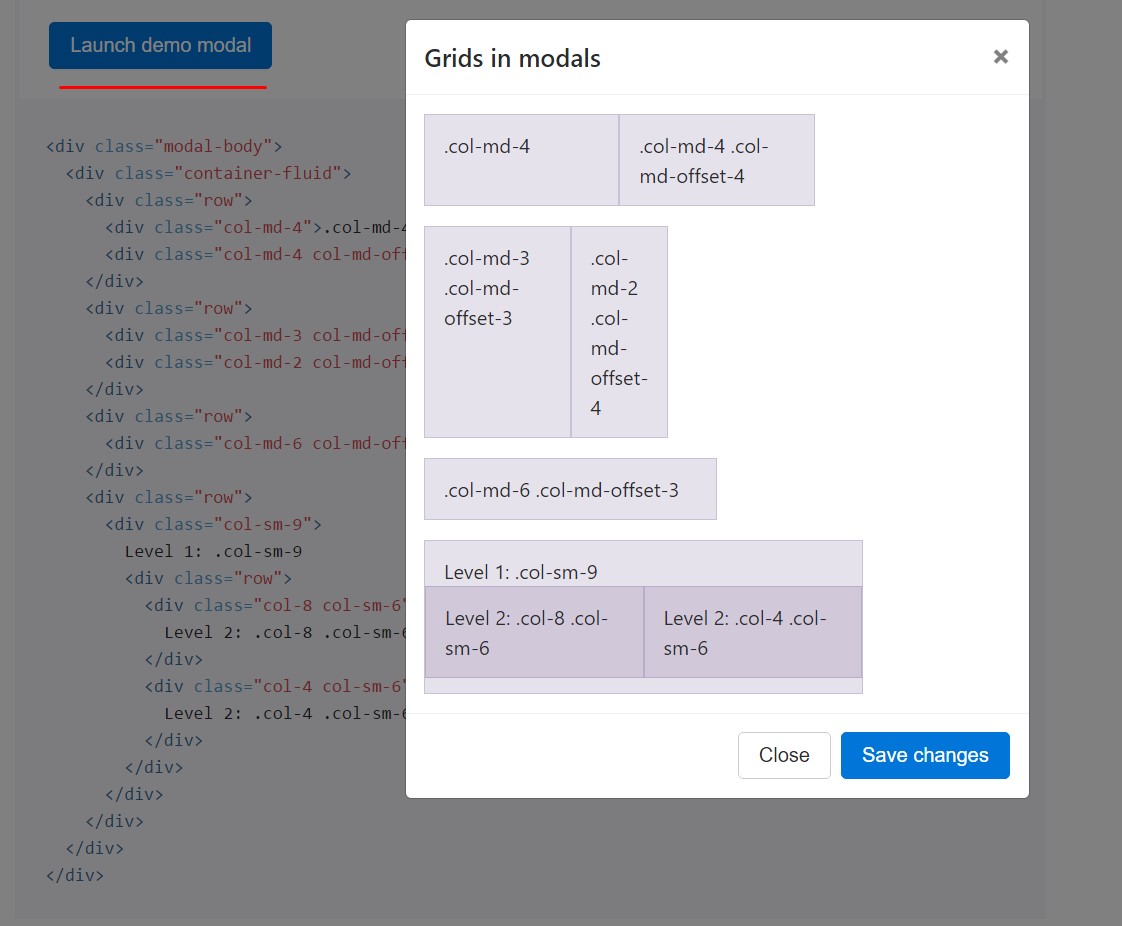
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-4 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-3 .col-md-offset-3</div>
<div class="col-md-2 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-2 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-6 .col-md-offset-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>A variety of modal web content
Contain a bunch of tabs that trigger the equal modal using just a little different contents? Employ
event.relatedTargetdata-*Shown below is a live demonstration followed by example HTML and JavaScript. To learn more, looked at the modal events files with regard to particulars on
relatedTarget
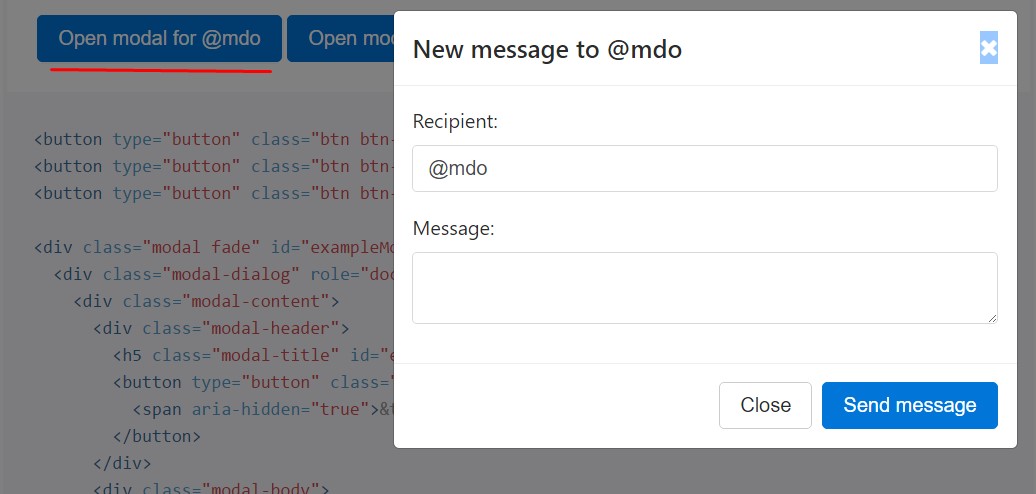
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@mdo">Open modal for @mdo</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@fat">Open modal for @fat</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@getbootstrap">Open modal for @getbootstrap</button>
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">New message</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="recipient-name" class="form-control-label">Recipient:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="recipient-name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message-text" class="form-control-label">Message:</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="message-text"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Send message</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>$('#exampleModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event)
var button = $(event.relatedTarget) // Button that triggered the modal
var recipient = button.data('whatever') // Extract info from data-* attributes
// If necessary, you could initiate an AJAX request here (and then do the updating in a callback).
// Update the modal's content. We'll use jQuery here, but you could use a data binding library or other methods instead.
var modal = $(this)
modal.find('.modal-title').text('New message to ' + recipient)
modal.find('.modal-body input').val(recipient)
)Delete animation
For modals which just simply pop up instead of fade in to view, take down the
.fade<div class="modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="..." aria-hidden="true">
...
</div>Lively levels
If the height of a modal switch moment it is exposed, you must call
$(' #myModal'). data(' bs.modal'). handleUpdate()Availability
Adding YouTube web videos
Implanting YouTube video clips in modals demands extra JavaScript not with Bootstrap to immediately stop playback and even more.
Optional proportions
Modals possess two optionally available sizes, available with modifier classes to be put on a
.modal-dialog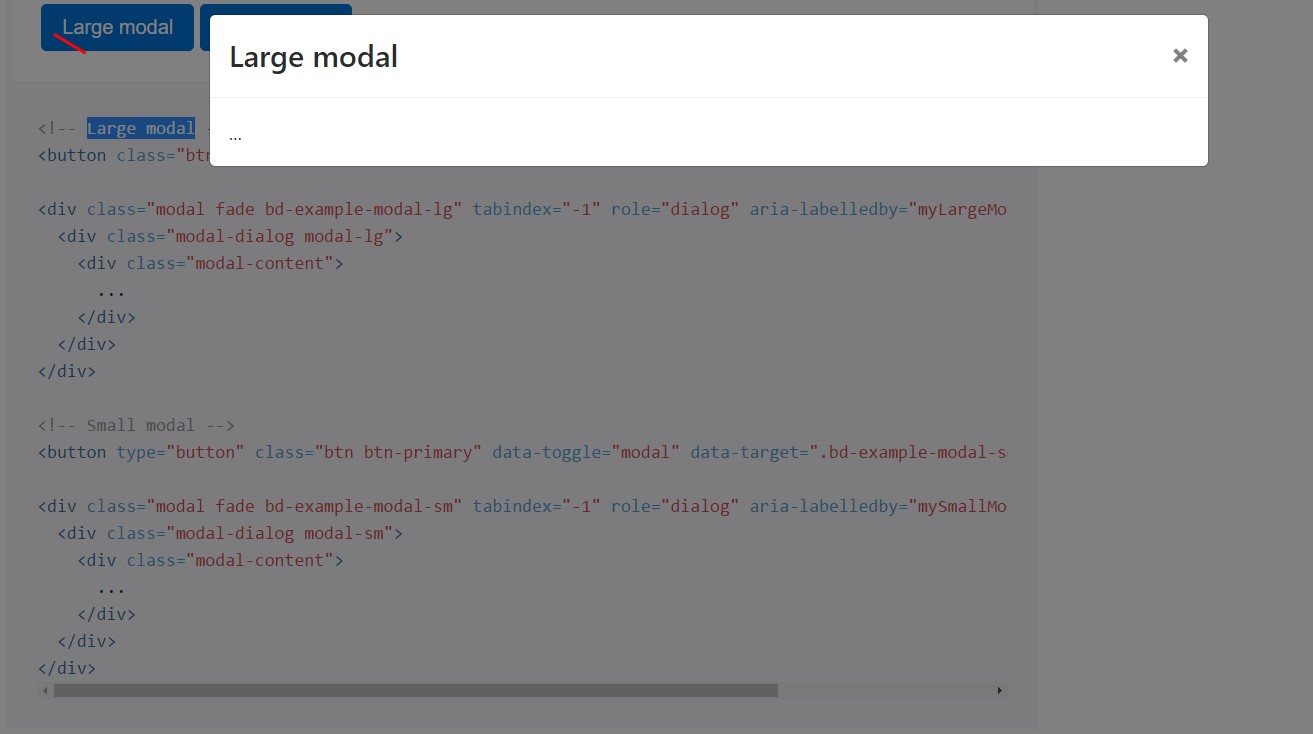
<!-- Large modal -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-lg">Large modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-lg" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myLargeModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-lg">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>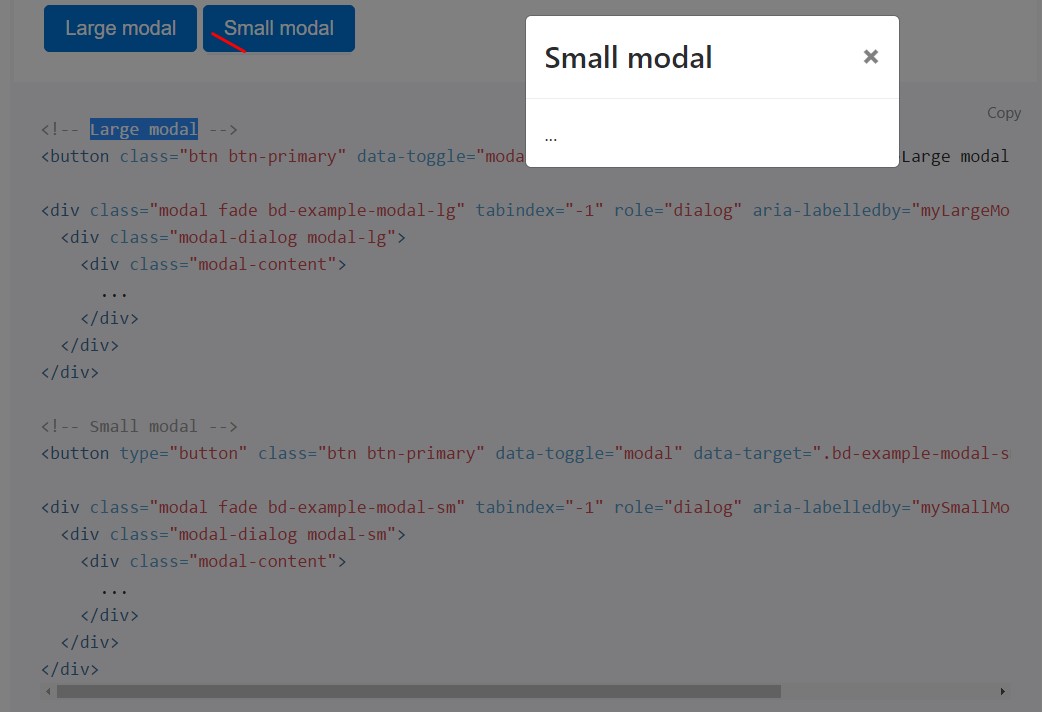
<!-- Small modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-sm">Small modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-sm" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="mySmallModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-sm">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>Operation
The modal plugin toggles your hidden content on demand, via data attributes or JavaScript.
Using files attributes
Turn on a modal without any preparing JavaScript. Set
data-toggle="modal"data-target="#foo"href="#foo"<button type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#myModal">Launch modal</button>Using JavaScript
Call a modal using id
myModal$('#myModal'). modal( options).Possibilities
Opportunities can possibly be passed via information attributes or JavaScript. For information attributes, append the option name to
data-data-backdrop=""Take a look at also the image below:
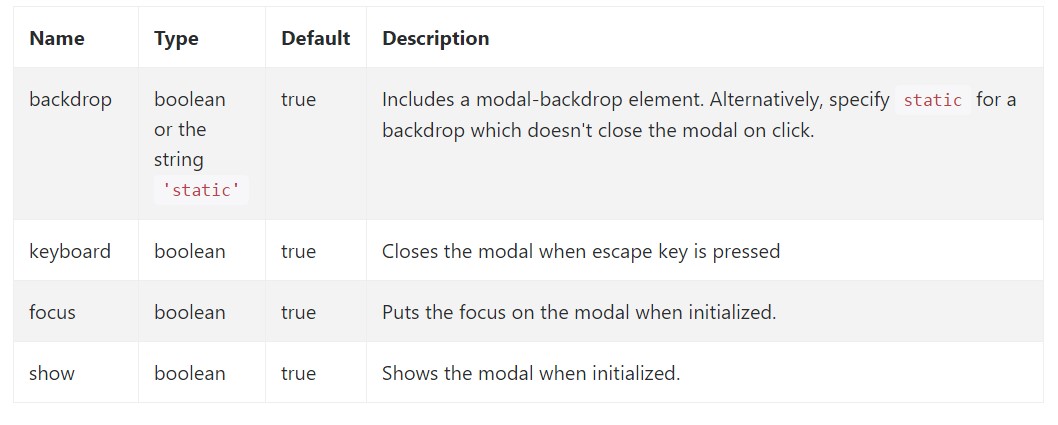
Practices
.modal(options)
.modal(options)Triggers your information as a modal. Accepts an optionally available options
object$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
.modal('toggle')Manually toggles a modal. Go back to the caller just before the modal has actually been shown or hidden (i.e. before the
shown.bs.modalhidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
.modal('show')Manually begins a modal. Returns to the user right before the modal has really been displayed (i.e. before the
shown.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
.modal('hide')Manually conceals a modal. Come back to the caller before the modal has truly been covered up (i.e. just before the
hidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class reveals a few events for trapping inside modal capability. All modal events are fired at the modal itself (i.e. at the
<div class="modal">
$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Conclusions
We found out just how the modal is built but just what would probably be inside it?
The answer is-- almost anything-- coming from a long words and conditions plain paragraph with some headings to the very most complex building that utilizing the adaptative design concepts of the Bootstrap framework might literally be a web page inside the page-- it is actually possible and the option of applying it is up to you.
Do have in mind however if ever at a certain point the information to be poured into the modal gets far too much probably the more desirable technique would be inserting the entire subject into a separate web page in order to gain basically improved visual appeal plus utilization of the entire screen width available-- modals a meant for more compact blocks of content prompting for the viewer's interest .
Examine several video clip information relating to Bootstrap modals:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap modals: formal documents

W3schools:Bootstrap modal tutorial
Bootstrap 4 with remote modal